KDM is a world-class laser cutting parts manufacturer for different industry applications
Designed through our advanced machinery and modern procedures
- KDM has above 10 years in the industry of manufacturing best laser cutting parts
- KDM has a supplier of eco-friendly laser cutting parts in China
- Modern designed laser cutting parts to exceed your diverse expectations
- 24/7 available customer service
Experienced Laser Cutting Parts Supplier in China
KDM offers high durability and effective laser cutting parts. We assure to meet the processing requirements for different industries highly demanded by most clients. Accurate dimensions laser cutting parts, resistance to rust, adverse temperature, and more.
KDM ensure that your laser cutting part orders reach the top products in the market.
KDM Laser Cutting Parts Series
Over many years of manufacturing high-quality Laser Lenses in China, we have been trusted by most of clients. We provide laser lenses with long life and low-cost.
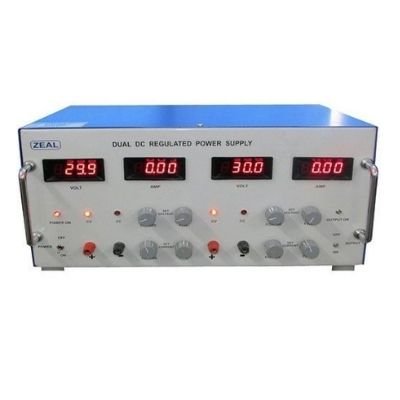
KDM manufactures a regulated power supply which is equipped with a voltage selector and an OFF/ON indicator lamp. For more details about our regulated power supply, contact our sales representative today!
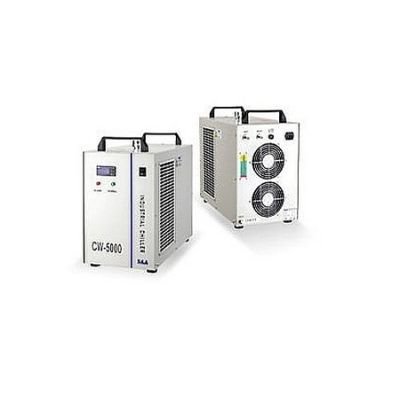
KDM is a certified manufacturing organization offering a wide array of water chiller. Trust KDM to be your number one water chiller manufacturer and supplier!
Send your Inquiry on KDM Commercial Mail Boxes
KDM provides turnkey solutions for your laser cutting parts demands. Our well-trained engineers and designers can help you meet your ideal laser-cutting specifications for your project requirements.
- Unlimited stocks which will provide client’s necessity
- Economical laser cutting parts are offered
- Latest machines are utilized to produce massive number laser cutting parts
- Laser cutting parts tested with caution by knowledgeable QC team
Related Products of Laser Cutting Parts
KDM Laser Cutting Parts
KDM laser cutting parts meets the processing requirements of various industries.
We are offering an excellent quality laser cutting parts.
Our laser cutting parts are highly demanded and appreciated by most clients owing to its rugged construction, top-notch quality, and extended durability.

KDM laser cutting parts is designed for servicing and assembling of the system or complex machines.
To manufacture our laser cutting parts, our top-notch engineers have used a superior quality raw material.
For that reason, our laser cutting parts we deal with ensures durability and strength.
We have laser cutting parts that are widely used for fabrication and fastening purposes in numerous industries.
The offered products ensure accurate dimensions.
Our laser cutting parts is resistant to rust, adverse temperature, pressure, and other such factors.

In our factory, you can find different shapes, sizes, and designs of laser cutting parts that fit your applications according to your needs.
Plus, we can customize your laser cutting parts as per specifications.
KDM laser cutting parts are designed to resist high temperature and extreme working conditions.
Being a popular supplier and manufacturer in this industry, KDM is able to offer a wide range and excellent quality laser cutting parts throughout the world.
It is fabricated under the guidance of our quality professionals utilized in using high grade materials and modern technology.
Being precision-engineered, KDM laser cutting parts are extensively used in electronics and automobile industries.
Also, it is best suitable for various industrial operations.

What’s more, in order to fit the specific requirements of our customers, KDM offers standard laser cutting parts.
With the help of our expert and skilled professionals and advanced manufacturing facility, we are recognized in supplying and trading a wide array of laser cutting parts in China and throughout the world.
The laser cutting parts we offer are being constructed upon the perfect needs of our clients.
Our expertise is progressed for custom laser cutting parts that meets to ISO 9001 quality standards.
The laser cutting parts we offer are available in numerous grades and sizes.
It is rigidly tested and checked to any quality parameters to ensure its quality.
For more than 10 years, we became a trusted supplier and manufacturer of laser cutting parts in China which are exported to any country.
Since we are registered to quality system ISO 9001, KDM guarantees you that all of the laser cutting parts we deal are defect-free with compact tolerance you need.
For more information about our laser cutting parts,do contact us today!
Laser Cutting Parts – The Complete FAQ Guide
Laser cutting is quite a new technique of metalworking.
It utilizes the force and produced the heat of lasers to achieve the most accurate results.
If you are wondering what is laser cutting and how can it be used to produce high qualitative metal parts, please, continue reading this FAQ guide.

What is meant by the laser cutting process?
As you may guess from a name, laser cutter utilizes a laser to cut various materials without contact.
Laser cutting procedure is widely used in different industries due to high quality and accurate results.
The process itself can be described as follows:
- The laser beam is directed through a nozzle to the workpiece.
- A combination of heat and pressure creates the cutting action.
- The material melts, burns, vaporizes or is blown away by a laserjet, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish.
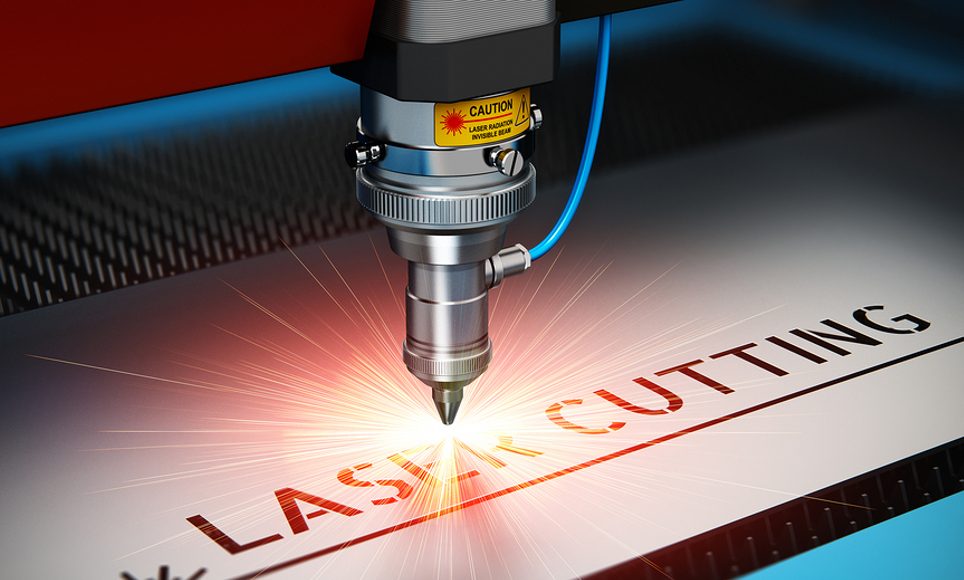

What are the main materials used to produce laser cutting parts?
At KDM Steel, we have a huge variety of metals that can be used to produce laser cutting parts:
- Steel (including acero inoxidable).
- Nickel.
- Brass.
- Copper.
- Aluminum.
Our specialists mainly use sheet metal when manufacturing laser cutting parts.
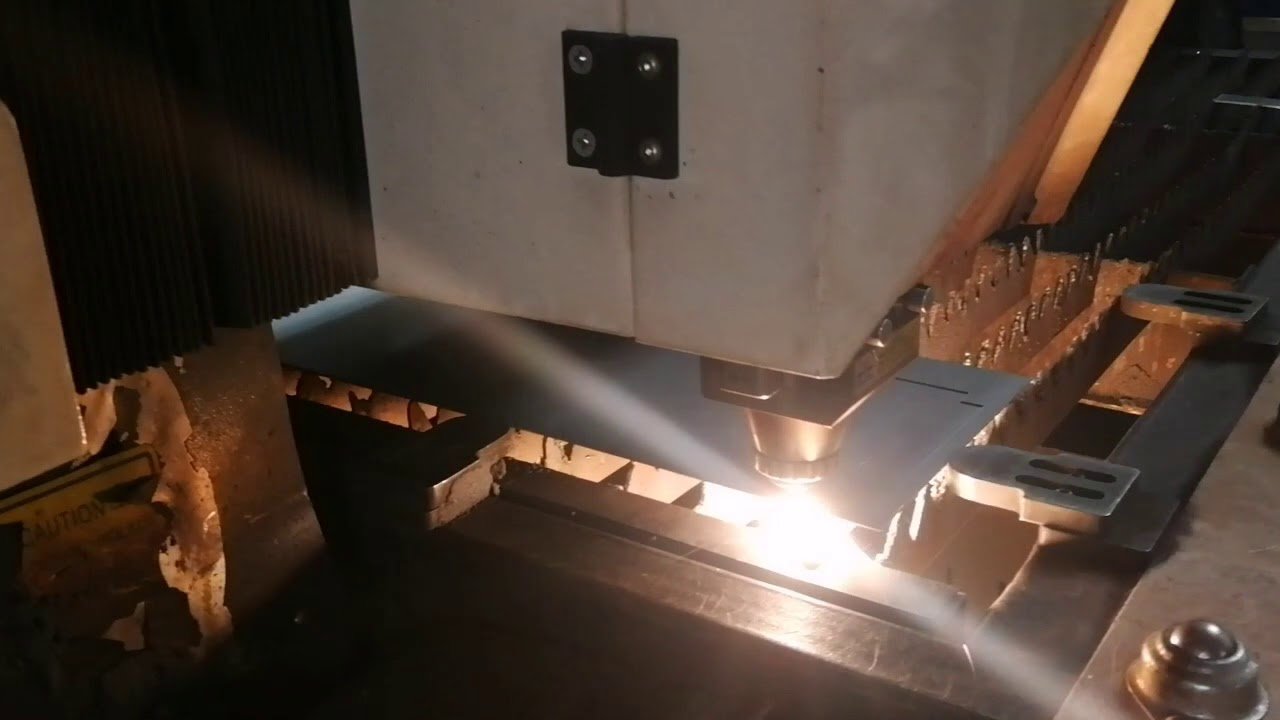
How thick can a laser cut?
However, this process is somewhat limited in the material thickness it can cut.
Speaking of a 4,000-watt laser, 3/8-inch carbon steel usually is the thickest steel used.
When we are talking about a 6,000-watt laser, the same material’s thickness might be increased to 1/2 inch.
Note: keep in mind that the above-mentioned values are approximate and refer to one type of material only (in this case, carbon steel).
Such numbers differ significantly from one material to another, so you can require about Acero KDM capacities to be precise.

In what industries can laser cutting parts be used?
What are the requirements for parts in various industries?
Laser cutting can be effectively used across a wide range of industries including electronics, automotive, medical, metalworking, printing, packaging, HVAC and other specialty industries.
Let’s have a closer look at some of them.
# 1. Aerospace industry
This huge area is one of the greatest utilisers of precision engineering, reliant on laser cut metal due to the exactness and versatility.
Aircraft can consist of incredible small parts with microscopic holes that need to be drilled.
Heavy-duty aluminum alloys and various rare metals are often required to be cut with the lowest heat-effect zone, as well as with flawless finish.
It is logical that not all cutting machines can be used to satisfy special needы of the aerospace industry.
However, due to significant accuracy laser cutters are perfect for such an application.
Apart from the production of airplanes, this industry also uses laser cutting for everything from combustor liners, to metal detectors, trolleys, conveyors, and stillages.
# 2. Automotive industry
As well as the previous example, the automotive industry couldn’t exist without small and complex parts engineered reliably with the help of laser cutting methods.
Laser cutting can be used to produce various shapes cleanly.
What is more important, laser cutters are capable of processing 3D details for exhaust systems, engines, and other car systems.
# 3. Electronics
The already mentioned unique ability to cut complex parts and small components make laser cutters an ideal tool for the electronics industry.
Electronic products become increasingly smaller each year, which is exactly the job of ultra-precise laser cutting machines.
Because laser cutters are so accurate, they require practically no extra space to cut around any components.
This allows such things as circuit boards y chips to be manufactured in the smallest dimensions possible.
Let’s not forget that laser cutters also used to manufacture finished electronic products, such as highly polished metal cases for mobile phones, laptops, and personal computers.
# 4. Medical tools
When lives depend on the quality of equipment, consistency and precision are the musts.
The creation of proper medical devices is one of the most frequent uses of laser cutters, and maybe the most needed for our society.
For example, high-grade stents used to relieve kidney stone pain and birth control measures are routinely cut by laser.
Lasers are needed to produce a variety of hospital supplies, such as stainless steel bed frames and trolleys, as well as aluminum machinery parts and brackets, valve framers, bone reamers, vascular clips, and flexible shafts.
As with the aerospace industry, the medical sector often requires the use of exotic metals that are difficult to cut.

How about the size of laser cutting parts produced by KDM Steel?
Are there some limitations?
When it comes to the size of laser cutting parts, the vast majority of companies speak about the magnificent feature of laser cutters to cut tiny parts.
However, it is more important to figure out the maximum size of the part, because various industries rely on parts of different size.
For example, the medical industry most often requires small parts and various medical tools, e.g. scalpels, tweezers, clamps, etc.
The aerospace industry, on the other hand, might require both small and big parts.
What is the problem with big parts, you might ask?
It comes from the construction of laser cutters: each machine has a so-known bed, where the piece of metal is put for further cutting.
And as you may assume, the size of the bed differs from one machine to another.
At KDM Steel, the size of laser cutting bed is 18” x 32”, which is the maximum sheet size we can cut.
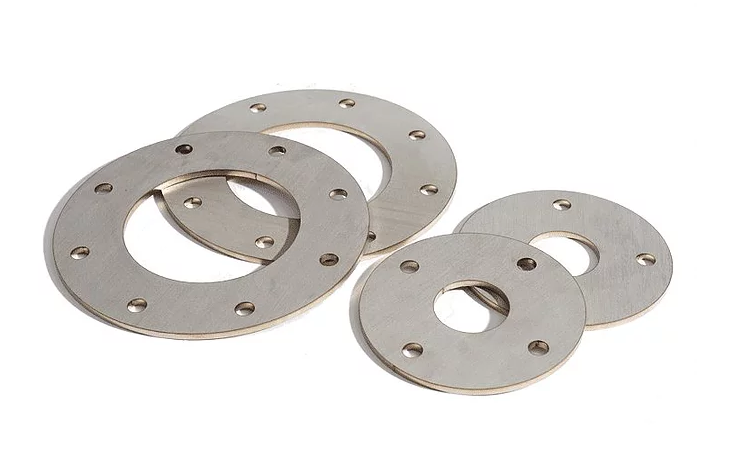

Can KDM Steel produce 3D laser cutting parts?
KDM Steel staff is equipped with 10 types of stainless steel laser cutting machines, that have various manufacturing capabilities.
Our laser cutting machines can easily process both thin and thick sheet metal.
Finally, at KDM Steel, we can do 2D and 3D laser cutting with a similar precise fashion.
How accurate is cutting with lasers when making parts?
The short answer is extremely accurate.
In practice, laser cutter’s accuracy is the major advantage over other cutting machines.
The laser cutter is able to make precise cuts, so the final part will look clean and smooth.
The precision of laser cutter also gives you another advantage: due to smooth processing you can place more parts in the metal blank.
In other words, you can get more products out of a single piece of material.
For better processing, the laser cutter’s intensity ratios and the speed of the cut can be adjusted.
So no matter what material you’re cutting, you can achieve the same accurate results.
Despite the fact that the laser beam is thinner than any other metalworking tool, still, it has some thickness.
When the laser cuts through the blank, some portion of the material might be lost due to melting.
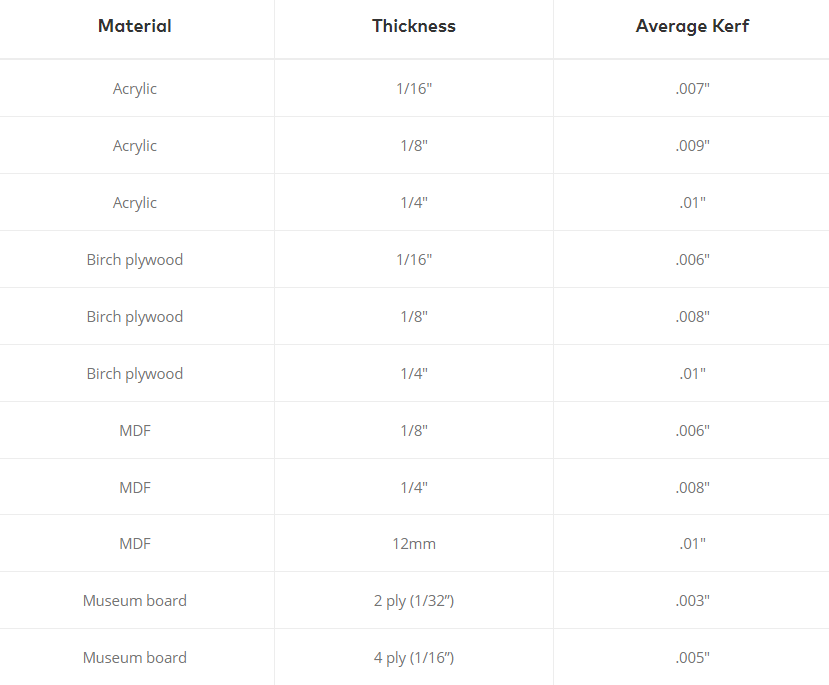
This portion in the form of thickness is called a kerf.
For most applications of laser cutting parts, this value might be unimportant.
However, when we are talking about tiny details and other custom projects, adjusting the drawing for the kerf of the laser may be necessary.
For example, if a design has a slot and fills components that rely on the friction of materials, adjusting for the kerf of the laser would be a good idea.
Below is a list of average kerfs for some of our materials and thicknesses.
These numbers are to be used as a guideline to base your design from and not absolute measurements.
If you need to, you can get a few samples and prototype the design first, and then tweak accordingly.
Are there different types of laser cutters?
Which laser machines are best for cutting metal parts?
There are four main types of laser cutters available:
- The CO2 laser cutter (mainly used for cutting, engraving, and boring).
- The neodymium (Nd) laser cutter (used for high energy and low repetitive procedures, as well as for boring).
- The neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd-YAG) laser cutter (same as the Nd laser when it comes to style but Nd-YAG is used for boring and engraving where high power is required).
- Fiber laser cutter (is made from a “seed laser”, and then amplified via special glass fibers. The lasers have an intensity and wavelength similar to that of the neodymium lasers, but because of the way they are built, they require less maintenance).
Let’s mention that all three aforesaid types of lasers can also be used for welding.
CO2 lasers are used for industrial cutting of various materials such as wood, mild steel, glass, acrylic, leather, paper, wax, plastics, various fabrics.
Their working principle is based on a carbon dioxide gas mixture, that is stimulated by electricity.
The most popular type of CO2 lasers is those which use the radiofrequency method.
While the CO2 lasers work with the help of gas, Nd and Nd-YAG lasers’ working principle is based on the utilization of crystal materials.
Such laser cutters are mostly used for cutting metals and ceramics since they have more power.
Pumped by diodes, these lasers contain very expensive parts that must be replaced after 15 000 hours of use.
So, it is logical that the use of crystal laser cutters cost significantly more than in the case of CO2 cutters.

Can you give some advice on how to design laser cutting parts?
# 1. Localized hardening
Lasers cut by melting or vaporizing metal.
This can create problems when cutting heat treatable materials as the area around the part will become case hardened.
Laser-cut holes in stainless steel or heat treatable steel alloys that require machining (tapping, countersinking or reaming) can be particularly troublesome.
By the same token, designers can employ this characteristic to their benefit when a product must be case hardened for wear resistance.
# 2. Edge taper
The laser is most accurate where the coherent light beam enters the workpiece.
As the beam penetrates the part, the light scatters creating an edge taper condition similar but opposite from “breakout” in a sheared or pierced part.
The hole on the side of the workpiece from which the laser beam exits is generally smaller in diameter than the entrance side.
Thus the designer must carefully consider the final use of the part and, in some cases, may have to specify from which side the part should be cut.
# 3. Minimum through-feature size
The cutting laser beam is focused down to approximately 0.010 in. (0.2 mm) and is therefore capable of cutting holes and features with radii approximating 0.030 in. (0.76 mm).
The limits applicable to piercing or blanking with a punch and die, such as the relationship between minimum hole size and material thickness, or the minimum distance between features to avoid distortion, do not apply when laser cutting.
# 4. Micro-tab
Holds part in the sheet while processing, generally removed after processing.
It can be strategically located so removal not necessary, resulting in cost savings.
The general size of micro-tab would be .25mm-.5mm.
Since no mechanical force is applied, the width of material remaining between cutout features may be very narrow without distortion occurring during metal removal.
A typical application would be tightly spaced venting slots on a visually important surface.
Note: if you want KDM Steel to use your drawings, please, be sure that they consist only those lines which have to be cut.
Despite the fact that our specialists will additionally check your drawings before put them into work, you’ll be responsible for issues, connected with such drawings.

What is a laser cutting pattern?
In simple words, a laser cutting pattern is a ready-made drawing of how the metal sheet is needed to be cut.
As you may assume since the metalworking was invented humanity has cut tons of parts which might be similar to those ones you need right now.
So there is no need to create a separate drawing: you can just get one of laser cutting patterns from the Internet and send them to KDM specialists.
We also have patterns of our own, so in the better part of cases, there is no need for producing the design of future parts.

Can you recommend software to produce a laser cutting part design?
If you want to draw a 2D part, we highly recommend the next software:
- CorelDRAW (graphic design software with an extensive number of tools and applications).
- Adobe Illustrator (powerful software used to create high-quality designs).
- AutoCAD (great drawing software, primarily used by engineers and architects to create detailed drawings and product representations).
- Inkscape (free open source option to make a simple graphic design).
- DraftSight (free option for professional 2D drafting and design solutions).
- LibreCAD (free open source software, community-driven 2D CAD program).
When it comes to designing 3D parts, you can try to use the following software:
- Solidworks (engineering 3D design software with multiple packages for aiding in design for specific applications).
- Autodesk Inventor (professional mechanical design software used to create and optimize designed systems).
- Autodesk Fusion (cloud-based CAD platform used to help designers through the engineering and manufacturing processes).
- Autodesk 123D Make (free software that allows you to import 3D models and slice them into laser-cut sheets that can be cut out and assembled).
No matter what kind of software is used, please remember about some of the most common file formats include:
- AutoCAD DXF.
- EPS in Adobe Illustrator.
- CDR by CorelDRAW.
- DWG by AutoCAD.
- SVG by XML.
- AI by Adobe Illustrator.

Can KDM Steel perform laser rastering and vector cutting?
Before we answer the question, let’s become familiar with laser rastering and vector cutting definitions.
# 1. Vector cutting
During a cutting operation, the cutting head fires a continuous laser at the material to slice through it.
In order to know where to cut, the laser cutter driver reads all of the vector paths in the designed piece.
Once you send your file to a laser cutter, only lines that register as the only hairline or vector graphics with the smallest possible line thickness will be cut by the laser.
All other graphics, like any images or thicker lines, will be rastered, which we’ll explain in a bit.
The laser, when supplied with the right settings, will cut through your material, so vector cutting is normally used for cutting out the outline of the part as well as any features or holes that you want to cut out of the material.
# 2. Laser rastering
Rastering is a lot different than vector cutting; instead of cutting through the workpiece, the laser will burn off the top layer of the material you are cutting to create two-color (and sometimes grayscale) images using the raster effect.
To raster materials, the laser will usually be set to a lower power than it would when vector cutting material, and instead of shooting down a pulsing beam, it creates fine dots at a selected DPI (dots per inch) so that the laser doesn’t really cut all the way through.
The DPI directly correlates to the image resolution and affects how fine an image appears, exactly like image resolution on a computer.
By adjusting the DPI you can control the laser’s effect on the material.
Rastering on some materials comes out really clearly, while you may not get exactly what you expected on other materials.
Before you raster for the first time, make sure you experiment with the settings until you get the desired effect.
Note: KDM Steel can perform all imaginable metalworking operations, including vector cutting and laser rastering.
Can you engrave laser cutting parts?
While cutting and engraving are two separate laser processes, they have many similarities, and so a single cutting laser setup can also be used to laser engrave materials too.
A cutting laser allows the user total control when it comes to beam intensity, duration and heat output, meaning that it can be manipulated to work with different materials and for different processes.
While the cutting and engraving processes are similar, they do have important differences.
First and foremost, laser cutting involves cutting into a material, whether to trim down its size or create shapes.
Engraving with lasers, on the other hand, concerns leaving a deep mark on a material, often used for things such as barcodes on items.
The difference between the actual conducting of the physical processes themselves comes down to the laser lens.
For the laser engraving process, you will find that the laser lens is shorter, which provides a finer and more precise spot size.
Due to this, the quality of the engraving is increased.
Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a longer laser lens, which is better for delivering a cut, especially on thicker metals and materials.
It will not be uncommon to have to perform both cutting and engraving on a single object or item, for example cutting down car pieces and then engraving serial numbers onto them.
At KDM Steel we can perform successfully both laser cutting and engraving procedures.

Laser cutting, plasma cutting, mechanical cutting – which way is better when making various parts?
While both plasma cutting and laser cutting offer a range of unique benefits, the ideal technique for a certain application will depend on the specifics of the job at hand.
For applications requiring tight part tolerances, laser cutting is usually ideal, as it utilizes a highly focused beam of light to complete cuts.
Laser cutting is also well-suited to parts requiring precise cuts or small hole diameters concerning the thickness of the material.
Laser cutting is typically used for thinner metals, while plasma cutters can handle thick sheet and plate metal.
Most modern plasma cutters can handle metals up to 80 mm thick.
For parts requiring simple, straightforward shapes without any cutouts or intricate notching, plasma cutting is a better option.
Plasma cutting can also cut metal with reflective surfaces, which cannot be handled by lasers.
Plus, plasma machines can be employed for many different purposes, such as scribing, trimming, welding, and engraving.
Plasma cutting equipment is generally more cost-efficient than laser machines — especially when dealing with high-end models — and ensures high-quality part replication.
Although plasma cutters have a smaller kerf than laser cutters – which means less material is lost during the profiling process – laser cutters allow for slightly tighter tolerances.
Both plasma and laser cutters can be easily integrated with CAD/CAM tools.
Due to the fact that laser cutting not only cuts the material but it applies a finish to a product, thus it can easily be said that laser cutting is a more streamlined process as compared to its alternative, mechanical cutting.
In laser cutting the chances of accidental marking or contamination is very less because there is no direct contact between the material and the laser device.
Also, lasers produce a smaller heat-affected zone which results in a lower risk of deformation and material wrapping at the cutting site.
However, laser cutting can be a very costly and complex fabrication method.
Mechanical methods, on the other hand, are very cost-effective and they can easily be incorporated into the manufacturing services.
Unlike laser equipment that requires a powerful energy source, mechanical require less energy source and they don’t consume energy as rapidly as laser equipment.
Laser devices are mostly peripheral equipment and they are expensive.
Machinery like lenses, zinc selenide, and gold mirror yield additional expense, nonetheless, they are very important for laser cutting method.
When choosing between mechanical and laser cutting, it imperative to remember that these processes are not exclusive of each other.
Choosing between one depends on what is your priority, saving cost and energy or reducing the chances of deforming and damaging of a given material.

How to process the surface of a part after laser cutting?
Initially, all metal blanks come unpolished, as a raw piece of metal.
After the laser cutting process is done, all metal parts can be burnished to achieve the best design.
Another important thing that can be done by KDM Steel specialists is engraving: after we cut the metal parts following your drawing, we can engrave some kind of marks on its surface.
Actually, engraving is a great tool for brands to individualize each metal part.
Can laser cause damage to the part?
In some cases, yes.
Even though industrial laser cutting machines come with various safety mechanisms, it is still possible to cause significant damage not only to the metal part but also to the human operators.
That is why KDM Steel specialists go through certain training programs before they can start working with laser cutters.
Speaking of the damage to metal parts, things become almost safe, especially in the modern era.
Due to special constructive solutions, laser cutting is a non-contact process and uses a beam that is highly precise on the area it is being focused upon.
So the heat damage is minimal to the surrounding area of the material.
https://youtu.be/SG8h1Ykf1lc









